Safety management system software transforms scattered spreadsheets and filing cabinets into centralised digital platforms. These tools capture incidents, track audits, assess risks, and manage compliance requirements across your entire operation.
Modern safety management software delivers measurable operational improvements. Organisations transitioning from manual processes can reduce administrative time by up to 40% and eliminate over 100,000 sheets of paperwork annually.
The right platform connects your safety team, frontline workers, and executive leadership. Everyone sees the same data. Everyone works from the same compliance requirements.

This guide examines the core capabilities that define effective safety management system software. You’ll discover how EHS software addresses incident management, compliance tracking, audit management, risk assessment, and safety training. We’ll explore mobile capabilities, dashboard analytics, and the business benefits that matter to operations teams.
By understanding these essentials, you’ll recognise which features support sustainable safety systems and which simply add complexity.
What Is Safety Management System Software?
Safety management system software provides a digital framework for documenting, tracking, and managing workplace safety activities. It replaces paper-based processes with structured workflows that guide safety managers through incident reporting, hazard identification, compliance verification, and corrective action management.

These platforms centralise safety data that previously lived in multiple locations. Incident reports, inspection checklists, training records, and audit findings exist within a single system. This centralisation eliminates the version control issues and data silos that plague spreadsheet-based approaches.
The software automates routine safety tasks. When someone reports an incident, the system automatically notifies the safety manager, assigns investigation tasks, tracks corrective actions, and generates required regulatory reports. This automation reduces administrative burden while ensuring consistent process execution.
Core Components of Safety Management Platforms
Safety management software typically includes several integrated modules. Each module addresses a specific safety function.
Incident management captures workplace injuries, near misses, property damage, and environmental releases. The module guides users through structured reporting forms, supports photo attachments, and tracks investigation progress from initial report through root cause analysis to corrective action closure.
Audit and inspection management schedules safety audits, distributes inspection checklists to mobile devices, captures findings with photos and comments, and tracks non-conformances through resolution. The module maintains audit history and generates compliance verification reports.
Risk assessment tools document hazard identification activities, evaluate risk levels using customisable matrices, and link control measures to specific hazards. The system tracks risk reduction progress and highlights high-risk areas requiring management attention.
How Safety Software Differs From General Business Tools
Safety management system software contains specialised functionality that general business platforms lack. The software understands regulatory frameworks like OSHA requirements, ISO 45001 standards, and industry-specific safety regulations.
These platforms include pre-built templates for common safety processes. OSHA 300 logs, incident investigation forms, safety audit checklists, and risk assessment matrices come standard. Safety managers don’t build these tools from scratch.
The software integrates with safety-specific hardware and data sources. IoT sensors monitoring air quality, wearable devices tracking worker location in hazardous areas, and environmental monitoring equipment feed data directly into the safety management platform.
Key Features of Safety Management Software
Effective safety management system software delivers specific capabilities that address the daily requirements of safety professionals. These features determine whether the platform supports or hinders safety operations.
Understanding which features matter helps you evaluate platforms effectively. Not every feature delivers equal value to every organisation.
Incident Management and Reporting
Incident management forms the foundation of most safety management software implementations. Workers need simple methods to report incidents immediately after they occur.
Modern incident management modules support multiple reporting channels. Workers submit reports through mobile apps, web browsers, phone hotlines, or kiosk terminals. This flexibility ensures reporting convenience regardless of work location or technology access.
The software captures essential incident details through structured forms. Date, time, location, personnel involved, witness information, injury type, and preliminary cause information get recorded consistently. Required fields prevent incomplete reports.
Photo and video attachments document incident scenes. Workers photograph equipment damage, hazardous conditions, or injury locations while still at the scene. This visual documentation supports thorough investigations.
Automated workflows route incidents to appropriate personnel. Serious injuries trigger immediate notifications to safety managers and executives. Minor incidents follow standard review processes. The system ensures no incident falls through administrative cracks.
Compliance Management and Regulatory Tracking
Compliance management capabilities help organisations maintain adherence to applicable safety regulations. The software tracks which regulations apply to specific operations, monitors compliance status, and generates required regulatory reports.
Regulatory libraries contain current versions of applicable standards. OSHA regulations, EPA requirements, DOT rules, and industry-specific standards exist within the platform. These libraries update automatically when regulations change.
Compliance calendars schedule required activities. Monthly safety inspections, quarterly emergency drills, annual training refreshers, and periodic equipment certifications appear on automated schedules. The system sends reminders before deadlines.
Electronic recordkeeping satisfies regulatory documentation requirements. OSHA 300 logs, training records, inspection reports, and equipment maintenance histories maintain required retention periods. The software provides audit-ready reports when inspectors arrive.
Audit Management and Inspections
Audit management modules streamline the planning, execution, and follow-up phases of safety audits and workplace inspections. These tools replace paper checklists with structured digital workflows.
The software maintains libraries of audit templates. Corporate safety audits, regulatory compliance inspections, contractor safety assessments, and equipment inspections use standardised checklists. Templates ensure consistent evaluation criteria across multiple locations.
Mobile audit capabilities allow inspectors to complete checklists on smartphones or tablets. Inspectors photograph non-conformances, add location tags, assign severity ratings, and capture corrective action notes while walking the facility. Offline functionality supports audits in areas without network connectivity.
Non-conformance tracking links identified issues to corrective action plans. Each finding receives assigned responsibility, target completion dates, and progress tracking. Dashboard reports show outstanding issues and overdue corrective actions.
Audit history provides trend analysis. The software compares current audit results to previous assessments, identifies recurring issues, and highlights improving or declining performance areas.
Risk Assessment and Hazard Management
Advanced risk management features allow companies to identify, assess, and mitigate workplace hazards in real time. These capabilities transform reactive safety approaches into proactive risk management systems.

Hazard identification tools capture potential risks before they cause incidents. Workers submit hazard observations through mobile apps. Safety committees document hazards identified during workplace inspections. The system maintains a comprehensive hazard register.
Risk assessment matrices evaluate hazard severity and likelihood. Customisable matrices align with organisational risk tolerance and industry standards. The software calculates risk scores automatically based on user inputs.
Control measure tracking links specific controls to identified hazards. Engineering controls, administrative procedures, personal protective equipment requirements, and training specifications connect to risk assessments. This linkage demonstrates how organisations manage specific risks.
Risk registers provide executive visibility into the organisation’s risk profile. Dashboard reports show high-risk areas, control effectiveness, and risk reduction progress over time.
Safety Training and Learning Management
Training management capabilities help organisations deliver, track, and document safety training programmes. These features ensure workers receive required training and maintain current certifications.
Safety management system software often includes learning management system functionality. Training content exists within the platform. Workers access courses through web browsers or mobile apps.
Training Scheduling and Tracking
The software maintains training requirements for different job roles. New hire orientation, job-specific safety training, equipment operation certifications, and periodic refresher training get assigned automatically based on position and work location.
Automated scheduling sends training assignments to workers. When someone requires training, they receive notifications with course access links. Managers receive reports showing incomplete training across their teams.
Training records document completion dates, scores, instructor names, and certification expiration dates. The system sends alerts before certifications expire. This proactive approach prevents workers from operating equipment with expired qualifications.
Competency Management Integration
Advanced platforms link training completion to competency verification. Workers demonstrate practical skills after completing theoretical training. Competency assessments confirm workers can safely perform high-risk tasks.
The software tracks competency assessment results alongside training records. This comprehensive documentation proves workers possess both knowledge and demonstrated ability to perform tasks safely.
Work permit systems can verify training and competency status. Before authorising someone to perform confined space entry, hot work, or lockout/tagout procedures, the system confirms they hold current training and competency certifications.
Mobile Capabilities and Offline Access
Mobile functionality extends safety management software to workers in the field. Construction sites, manufacturing floors, remote facilities, and mobile work crews require safety tools that work anywhere.
Mobile applications deliver core safety management capabilities on smartphones and tablets. Workers report incidents, complete inspections, submit hazard observations, and access safety procedures without returning to desktop computers.
Real-Time Field Reporting
Mobile incident reporting captures events immediately. Workers photograph accident scenes, record witness statements, and document equipment damage while details remain fresh. This immediacy improves investigation accuracy.
Location services automatically tag reports with GPS coordinates. Safety managers see exactly where incidents occurred. This spatial data reveals location-specific risk patterns.
Photo and video capabilities provide rich documentation. Workers capture multiple angles of hazardous conditions. Annotated photos highlight specific concerns. This visual evidence supports investigation teams.
Offline Functionality for Remote Operations
Offline mobile capabilities support safety management in areas without network connectivity. Underground mining operations, remote construction sites, and offshore facilities often lack reliable internet access.
Workers complete safety activities on mobile devices without network connections. Inspection checklists, incident reports, and hazard observations store locally on the device. When network connectivity returns, the mobile app synchronises data automatically with the central database.
This offline functionality ensures safety processes continue regardless of connectivity. Workers don’t skip inspections or delay incident reports because they lack network access.
Dashboard Analytics and Reporting
Dashboard capabilities transform raw safety data into actionable insights. Visual reports help safety managers and executives understand safety performance, identify trends, and make informed decisions.
Modern safety management software includes configurable dashboards. Users create custom views showing metrics relevant to their roles. Safety managers monitor incident rates and corrective action status. Executives track leading indicators and compliance metrics. Facility managers review location-specific performance.
Key Performance Indicators
The software calculates standard safety metrics automatically. Total recordable incident rate, days away from work rate, lost time injury frequency, near miss reporting rates, and audit scores update in real time as data enters the system.
Trend charts show performance over time. Monthly incident rates, quarterly audit scores, and annual training completion percentages appear as line graphs or bar charts. These visualisations reveal improving or declining performance.
Comparative reports benchmark performance across locations, departments, or work groups. Operations teams identify which facilities demonstrate superior safety performance and investigate contributing factors.
Predictive Analytics and AI-Generated Insights
Advanced platforms incorporate predictive analytics. The software analyses historical incident data, identifies risk factors, and highlights conditions associated with increased incident likelihood.
Machine learning algorithms detect patterns humans might miss. Correlations between incident timing, weather conditions, production schedules, and workforce composition become visible. Safety managers adjust programmes based on these insights.
AI-generated summaries translate complex data into plain language recommendations. Instead of interpreting multiple reports, managers receive automated briefings highlighting priority areas requiring attention.
Document Management and Control
Document management capabilities centralise safety documents within the software platform. Safety policies, standard operating procedures, emergency response plans, and regulatory documents exist in controlled repositories.
Version control prevents confusion about current procedures. When safety managers update a document, the system archives previous versions while making the current version immediately available. Users always access approved documents.
Policy Distribution and Acknowledgement
The software distributes updated policies to affected workers automatically. When a procedure changes, the system sends notifications requiring workers to review and acknowledge the updated document.
Electronic acknowledgement tracking creates audit trails. The system records who reviewed each document and when. This documentation proves workers received required policy updates.
Scheduled review cycles ensure documents remain current. The system alerts document owners when policies require periodic review. This proactive approach prevents outdated procedures from remaining in circulation.
Regulatory Document Storage
Safety data sheets, equipment certifications, training materials, and regulatory permits require organised storage with controlled access. Document management modules maintain these records with appropriate retention periods.
Search functionality helps users locate specific documents quickly. Full-text search, metadata filters, and document categories enable efficient retrieval. Workers find the safety data sheet they need without sorting through filing cabinets.
Chemical Management and SDS
Chemical management modules help organisations track hazardous materials throughout facilities. These tools maintain safety data sheet libraries, monitor chemical inventories, and ensure workers access current hazard information.
SDS libraries contain safety data sheets for all chemicals present in facilities. The software maintains current versions and archives historical sheets. When chemical suppliers issue updated safety data sheets, the system incorporates new versions.
Workers access safety data sheets through mobile devices or kiosk terminals. QR codes on chemical containers link directly to relevant safety information. This immediate access supports safe chemical handling.
Chemical inventory tracking monitors quantities and locations. The system maintains records of chemical storage areas, container sizes, and usage rates. This information supports emergency response planning and regulatory reporting.
Environmental Health and Safety Integration
Organisations increasingly adopt integrated EHS software platforms that address environmental compliance, occupational health, and workplace safety within unified systems. This integration eliminates data silos between safety, health, and environmental programmes.
Integrated EHS platforms share common data across modules. An incident involving a chemical spill triggers safety incident reporting, environmental release reporting, and occupational health assessment workflows simultaneously. This coordination improves response effectiveness.
Occupational Health Management
Occupational health capabilities track worker health surveillance, medical monitoring, and exposure assessments. The software schedules periodic medical exams, maintains health records, and monitors exposure to hazardous substances.
Integration with safety modules connects health data to incident investigations. When someone reports an injury, the system provides relevant medical history to support treatment decisions while maintaining privacy protections.
Exposure monitoring links workplace measurements to individual worker records. Noise exposure, air quality sampling, and biological monitoring results connect to affected workers. This tracking supports early intervention when exposures exceed acceptable levels.
Environmental Compliance Tracking
Environmental modules monitor air emissions, water discharges, waste generation, and resource consumption. The software tracks permit limits, calculates environmental metrics, and generates regulatory reports.
Shared workflows connect environmental and safety processes. Spill response procedures exist in both environmental and safety modules. Training requirements apply to both environmental and safety personnel.
Real-Time Data and Performance Monitoring
Real-time monitoring capabilities provide immediate visibility into safety performance. Dashboard updates reflect current conditions rather than historical reports.
Integration with IoT devices feeds sensor data into safety management platforms. Air quality monitors, gas detectors, temperature sensors, and noise meters transmit readings continuously. The software triggers alerts when readings exceed safe thresholds.
Wearable technology integration tracks worker location and physiological data. Heat stress monitors, fall detection devices, and proximity sensors send real-time data to safety systems. This monitoring enables rapid response to dangerous conditions.
Alert and Notification Systems
Automated alerts notify appropriate personnel when immediate action is required. Serious incidents, hazardous conditions, and overdue corrective actions trigger notifications to designated responders.
Escalation protocols ensure critical issues receive attention. If the primary contact doesn’t acknowledge an alert within specified timeframes, the system escalates to backup personnel. This redundancy prevents important notifications from being overlooked.
Communication tools within the platform support coordinated responses. Mass notification capabilities alert all workers during emergencies. Two-way messaging allows safety teams to coordinate response activities.
Cloud-Based Platform Benefits
Cloud-based safety management software delivers advantages over traditional on-premises systems. These platforms offer accessibility, scalability, and reduced IT infrastructure requirements.
Accessibility from any location supports distributed operations. Safety managers access the system from headquarters, remote facilities, or home offices. Mobile workers use the same platform through smartphone apps.
Automatic updates ensure everyone uses current software versions. Cloud providers deploy updates centrally. Organisations receive new features and security patches without managing software installations.
Scalability for Growing Operations
Cloud platforms scale easily as organisations grow. Adding new facilities, users, or modules doesn’t require hardware purchases or infrastructure upgrades. The cloud provider manages capacity increases.
Multi-site deployments benefit from centralised administration. Global organisations manage safety programmes across multiple countries through a single platform. Standardised processes coexist with location-specific requirements.
Integration Capabilities and APIs
Modern safety management software connects to other business systems through APIs. HR systems provide employee data. Maintenance systems share equipment information. ERP platforms supply work order details.
These integrations eliminate duplicate data entry. When HR hires someone, their employee record automatically creates a user account in the safety system. When maintenance schedules equipment inspections, those tasks appear in the safety management platform.
API connectivity supports custom integrations. Organisations connect safety software to industry-specific systems, proprietary databases, or specialised monitoring equipment.
Pricing Considerations for Safety Software
Safety management software pricing varies significantly based on features, user counts, and deployment models. Understanding pricing structures helps organisations budget appropriately.
Business plans typically range from $30–$60 per user per month, while enterprise plans offering advanced analytics and customisation cost $60–$100 per user per month. These subscription models include software access, updates, and support.
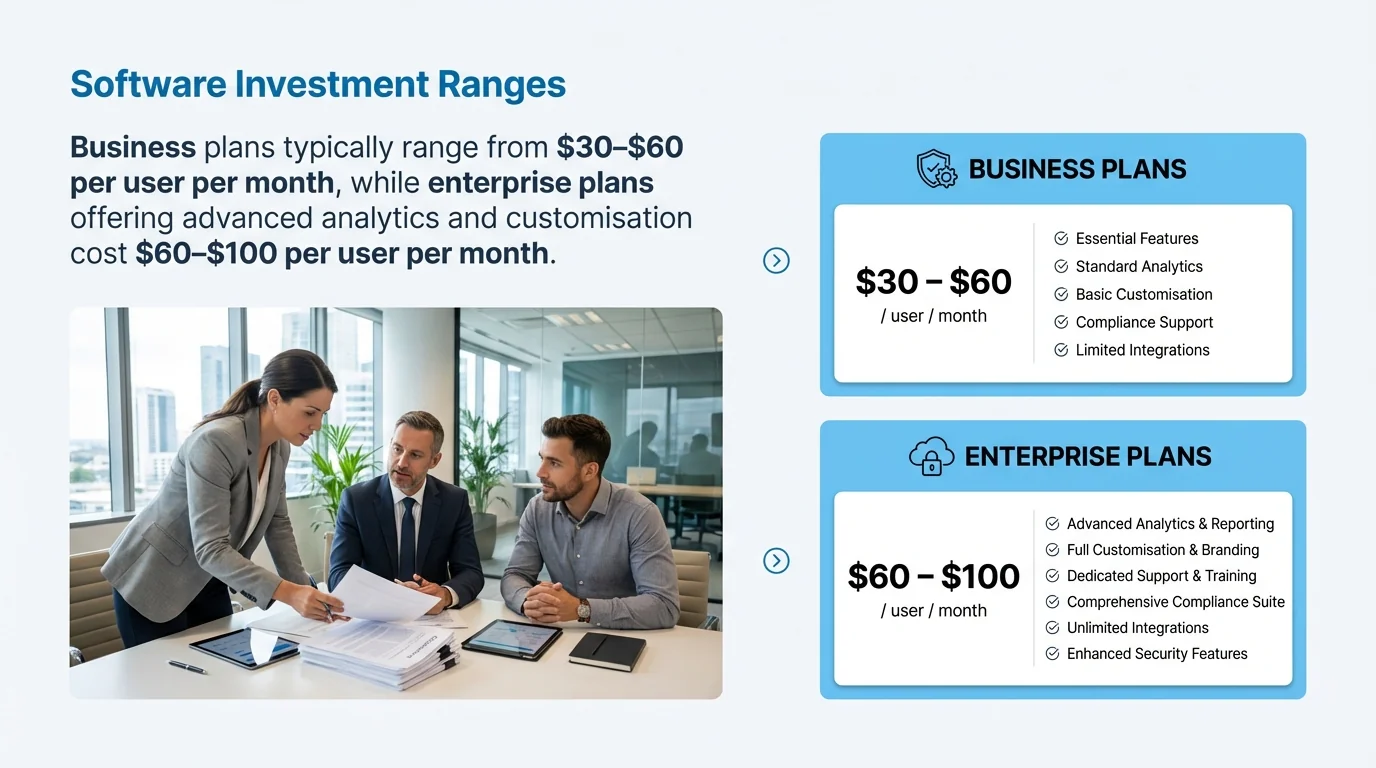
Some vendors charge based on facility count rather than user count. This pricing model benefits organisations with many users at few locations. Others price based on total employee count, including workers who don’t directly use the software but appear in reports.
Implementation and Training Costs
Initial implementation represents a significant investment beyond software subscription costs. Configuration, data migration, integration development, and training require time and resources.
Professional services from software vendors typically cost separately. Implementation consultants configure the system, migrate historical data, build custom reports, and train administrators. These services range from basic setup assistance to extensive customisation projects.
Ongoing support and maintenance costs continue after initial implementation. Software subscriptions include basic support. Premium support levels with faster response times and dedicated support contacts cost extra.
Selecting the Right Safety Management Software
Choosing appropriate safety management system software requires careful evaluation. The right platform aligns with organisational requirements, integrates with existing systems, and supports long-term safety objectives.
Start by documenting current safety processes. Identify which activities the software must support. Determine which features are essential and which are desirable but not critical.
Evaluate how well potential platforms match your industry requirements. Construction safety software emphasises different capabilities than manufacturing safety platforms. Ensure vendors understand industry-specific regulations and challenges.
Trial Periods and Demonstrations
Request demonstrations from shortlisted vendors. Ask them to show how their software handles your specific use cases. Prepare scenarios based on actual safety activities your organisation performs.
Negotiate trial periods before committing. Test the software with real users performing actual work. Gather feedback from safety managers, frontline workers, and executives who will use different system components.

Verify integration capabilities during trials. Confirm the software connects to your HR system, learning management platform, or other critical business systems. Test data exchange in both directions.
Vendor Evaluation Criteria
Assess vendor stability and track record. Established vendors with strong customer bases offer lower risk than startups with unproven products. Check customer references and review sites.
Evaluate support quality and availability. Determine support hours, response time commitments, and available support channels. Test their support responsiveness before purchasing.
Review the vendor’s product roadmap. Ensure their development priorities align with your future needs. Platforms that aren’t actively developing new capabilities may fall behind industry requirements.
Quick Answers to Common Questions
What is safety management software?
Safety management software is a digital tool that helps organisations manage workplace safety. It streamlines incident reporting, risk assessment, compliance tracking, and safety audits. Safety managers and HR professionals use these platforms to maintain regulatory compliance, reduce workplace risks, and improve safety performance through centralised data and automated workflows.
How does safety management software improve compliance?
The software maintains regulatory libraries with current standards, schedules required compliance activities, and generates audit-ready reports. Automated reminders prevent missed deadlines for inspections, training, and equipment certifications. Electronic recordkeeping satisfies documentation requirements and provides immediate access to records during regulatory inspections.
Can safety software work offline?
Modern safety platforms include offline mobile capabilities. Workers complete inspections, report incidents, and document hazards without network connectivity. Data stores locally on mobile devices and synchronises automatically when connectivity returns. This functionality ensures safety processes continue at remote sites and underground operations.